Agriculture, Forestry and Fishing - Economics and Employment
Explore the sector's economic data which highlights the contribution to the local economy on the Sunshine Coast.

The Agriculture, Forestry, and Fishing Industry on the Sunshine Coast plays a crucial role in the region's economy, contributing significantly to its growth and sustainability. Supported by the Sunshine Coast Regional Economic Development Strategy (REDS), this sector has shown remarkable resilience and adaptability. Despite recently facing labour challenges, the industry continues to thrive through strategic initiatives and technological advancements. This article draws on the most recent industry data to explore the sector’s current state, highlighting its strengths, opportunities for growth, and the vital role it plays in fostering a robust and sustainable economic environment on the Sunshine Coast. By focusing on upskilling the workforce and enhancing export capabilities, the region can ensure the continued success and stability of this essential sector.
Industry productivity
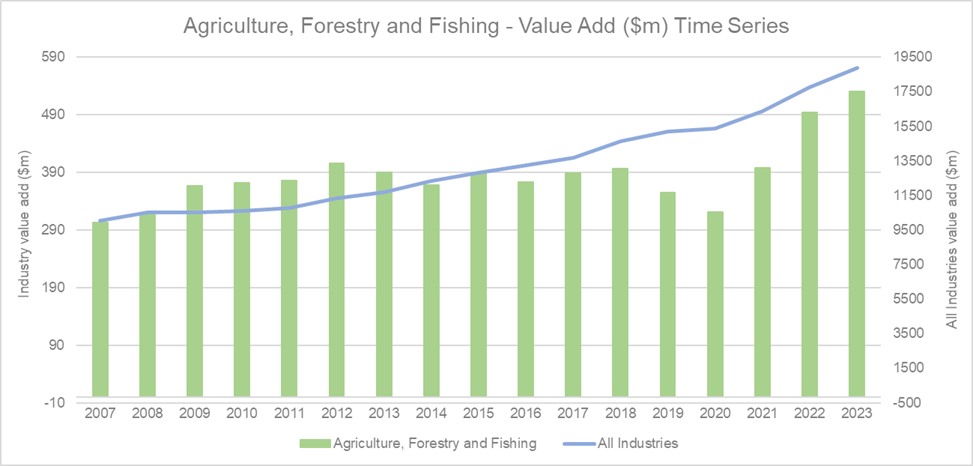
Source: National Institute of Economic and Industry Research (NIEIR) 2024. Compiled and presented by economy.id
The Agriculture, Forestry, and Fishing Industry on the Sunshine Coast has shown notable growth in value add, experiencing 7.3 per cent growth from 2022 to 2023. This contributed 2.8 per cent of total value added by all industries. Emphasis placed on agribusiness through the Sunshine Coast Regional Economic Development Strategy has supported the sector’s development in the region. This upward trend highlights the industry's resilience and potential for further development. Overall, growth in value added by all industries during the same period suggests a positive economic environment, which likely supports and enhances the performance of the Agriculture, Forestry, and Fishing sector. This growth can be seen as a promising sign for stakeholders and policymakers aiming to bolster the region's economic diversity and sustainability.
Industry workers qualifications
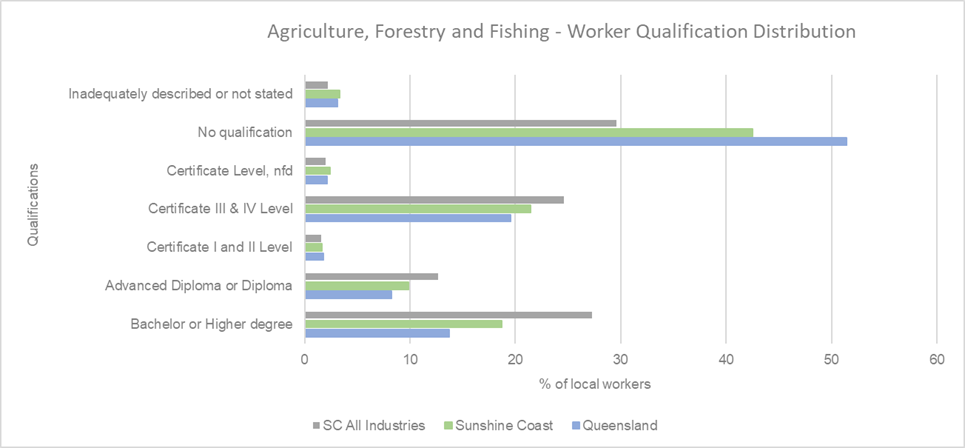
Source: Australian Bureau of Statistics, Census of Population and Housing 2021. Compiled and presented by economy.id)
A significant portion of workers in the sector have no formal qualifications, with around 45 per cent falling into this category. Higher education remains relatively low compared to all other local industries, although does outperform the Queensland average. This disparity suggests that while agriculture remains a vital part of the regional economy, there may be opportunities for growth through targeted education programs aimed at workforce upskilling. Enhancing qualifications could lead to increased productivity and innovation within these traditional sectors. This aligns with the REDS, which emphasises the importance of building a skilled workforce to support economic growth and sustainability. Investing in education and training can ensure that the agricultural sector remains competitive and capable of adapting to future challenges.
Total employment time series
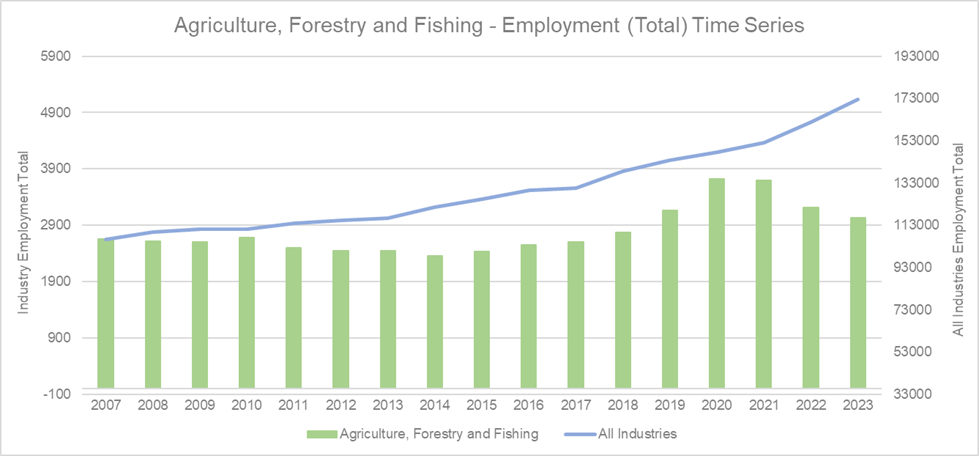
Source: National Institute of Economic and Industry Research (NIEIR) 2024. Compiled and presented by economy.id
The Agriculture, Forestry, and Fishing Industry contribute 1.8 per cent of employment opportunities in the region. Over the 2022 to 2023, total employment in the industry did decrease by 5.8 per cent. Labour shortages have been a contributing factor which has led to businesses in this industry investing in productivity improvements. This is represented in the ‘value add’ graph highlighted earlier in this article. The REDS outlines the importance of this sector in the region’s economic fabric. The strategy suggests that while automation can lead to job losses, it also presents opportunities for upskilling the workforce and improving productivity. By focusing on education and training, the region can help workers transition to new roles within the industry or other growing sectors, ensuring that the local economy remains resilient and adaptable to technological changes.
Export and local sales
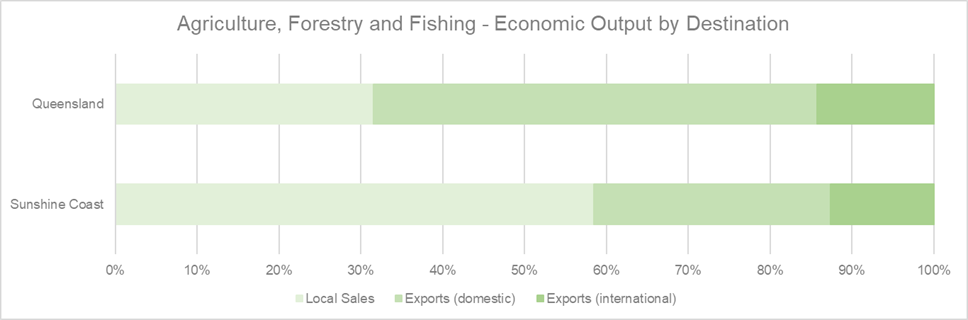
(Source: National Institute of Economic and Industry Research (NIEIR) 2024. Compiled and presented by economy.id)
The graph above illustrates the marginally higher percentage of local sales compared to Queensland, indicating a strong local market presence. Local sales make up 26.93 per cent of economic output by the sector. The Sunshine Coast industry is not as strong in interstate sales with national exports being 25.34 per cent less than Queensland. However, international sales are at a relatively similar level to the rest of Queensland. It’s highlighted in the REDS the need for initiatives to boost export capabilities and tap into broader markets. Continued support from local stakeholders such as the Food & Agribusiness Network, is essential to improving export performance and strengthening the sector’s economic resilience and sustainability.
Employee age and gender distribution
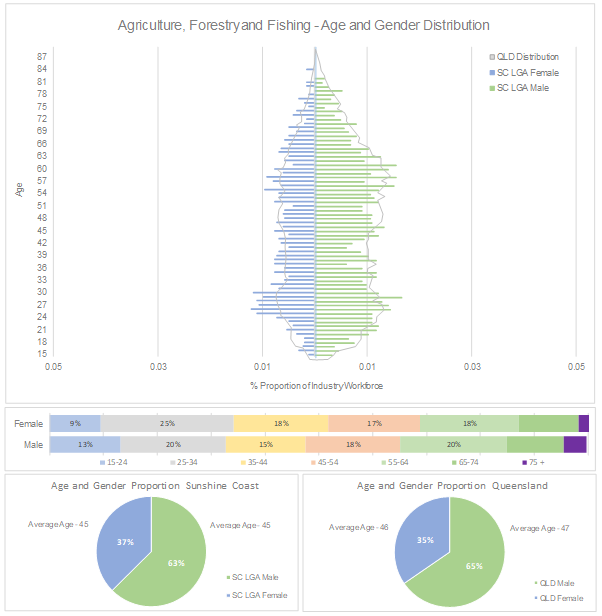
(Source: ABS Table Builder 2024, 2021 Census - employment, income, and education)
The population pyramid shows that a higher proportion of male workers work in the sector with 63 per cent male and 37 per cent female. This is comparatively similar to Queensland as a whole. The age distribution reveals that many workers are in the middle to older age brackets, with a noticeable concentration in the 45-54 age group. This trend suggests an ageing workforce, which could pose challenges for the industry in the future. The horizontal bar chart further emphasises the gender disparity, showing a higher percentage of males across all age groups. These trends highlight the need for targeted strategies to attract younger and more diverse workers to ensure the sustainability of the industry. Addressing these disparities through education, training, and recruitment initiatives could help build a more balanced and resilient workforce.
Industry business distribution
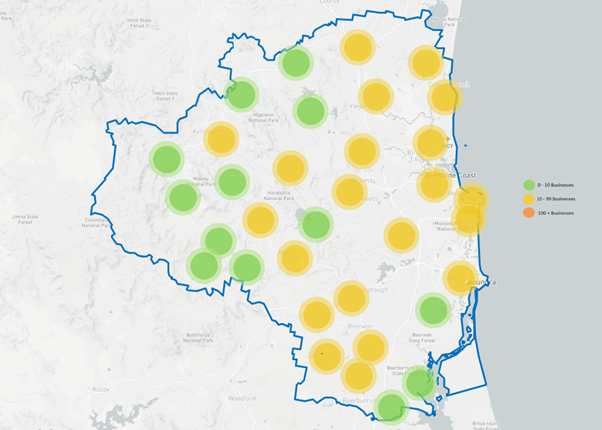
(Source: ABR 2024)
As an industry that utilises a spectrum of natural resources, businesses are spread widely across the Sunshine Coast region. Fisheries businesses can be found along the coastline. Inland and deep hinterland regions are home to agricultural businesses, while forestry can be found in the southern area.
Disclaimer: ABS employment Data has this information grouped by larger selected suburbs. Smaller suburbs feed into the data set of these selected suburbs.
Employee income distribution
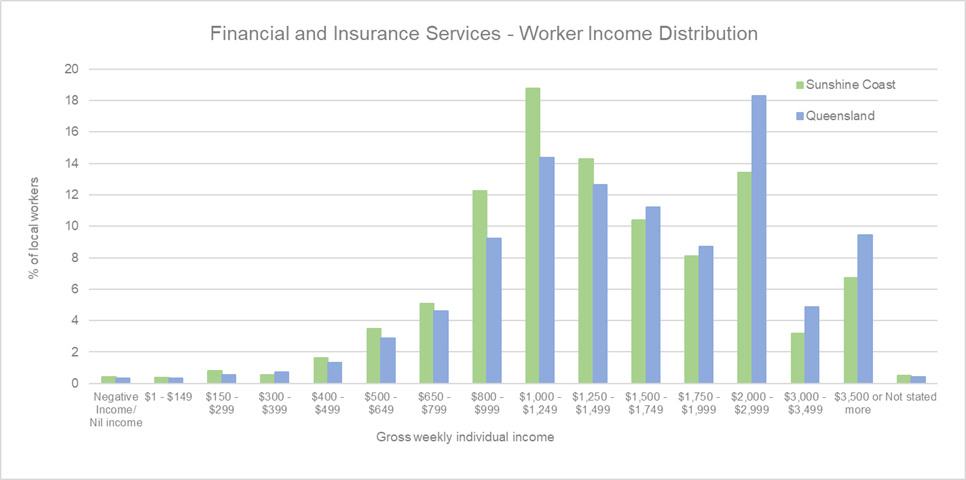
(Source: Australian Bureau of Statistics, Census of Population and Housing 2021. Compiled and presented by economy.id)
The attached graph illustrates the income distribution of workers in the Agriculture, Forestry, and Fishing industry on the Sunshine Coast compared to Queensland. It shows that approximately 43 per cent of workers in this industry on the Sunshine Coast earn under $799 per week. This highlights a significant portion of the workforce earning relatively low incomes. The largest group of workers, representing 18 per cent of the workforce, earns between $800 and $999 per week, as indicated by the tallest green bar in this range. In comparison, Queensland's distribution (represented by blue bars) shows a similar trend but with slight variations in percentages across different income brackets. This income disparity suggests that while the industry is vital to the local economy, there are opportunities to improve wage conditions. Aligning with the REDS, addressing these income disparities through targeted economic policies and workforce development programs could help enhance the overall economic well-being of workers in this sector. By focusing on increasing wages and providing better job opportunities, the region can ensure a more sustainable and equitable economic future for its agricultural workforce.
Conclusion
The Agriculture, Forestry, and Fishing Industry on the Sunshine Coast is a vital contributor to the local economy, showcasing significant contributions and benefits. The industry has demonstrated notable growth and resilience, supported by strategic initiatives under the Sunshine Coast Regional Economic Development Strategy (REDS). Its strong local market presence highlights its importance in providing for the local community, while still recognising the opportunities to come in domestic exports. The sector's ability to adapt through automation and productivity improvements ensures its continued relevance and efficiency. Focusing on upskilling the workforce and enhancing export capabilities will sustain local employment and also drive economic diversity and stability. These strengths underscore the industry's critical role in fostering a robust and sustainable economic environment on the Sunshine Coast.
Resources and support
- Food & Agribusiness Network
- Sunshine Coast Jobs Hub
- Workforce Evolve
- Level Up Your Business
- Sunshine Coast Regional Jobs Committee
Disclaimer
Information contained in this correspondence is based on available information at the time of writing. All figures and diagrams are indicative only and should be referred to as such. While the Sunshine Coast Regional Council has exercised reasonable care in preparing this information it does not warrant or represent that it is accurate or complete. Council, its officers, and contractors accept no responsibility for any loss occasioned to any person acting or refraining from acting in reliance upon any material contained in this document. Any forecasts or projections used in the analysis can be affected by a number of unforeseen variables, and as such no warranty is given that a particular set of results will in fact be achieved. Sunshine Coast Regional Council has referenced a range of data sources to compile this information including the Australian Bureau of Statistics, Queensland Government Statistician’s Office, Tourism Research Australia, Economy Id and the National Institute of Economic and Industry Research. While every care has been taken to ensure the content is accurate, there may be errors or omissions in it and no legal responsibility is accepted for the information.
